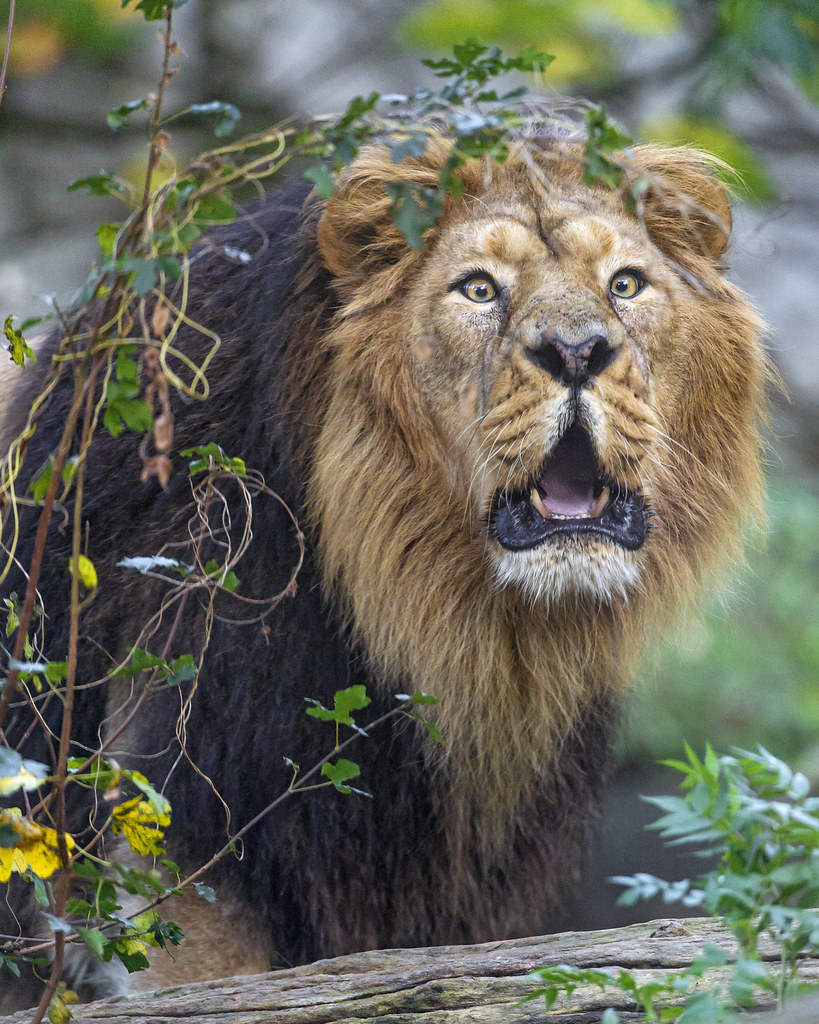
Asiatic Lion: Nestled within the arid landscapes of the Gir Forest in western India, the Asiatic Lion (Panthera leo persica) reigns as a symbol of strength, resilience, and the untamed beauty of the wild. With a storied history and a unique presence, the Asiatic lion stands as a testament to India’s commitment to the conservation of its endangered species.
“Embark on a captivating exploration of the Asiatic Lion, a symbol of regal strength and resilience. Uncover the mysteries of their natural habitats, unique behaviors, and the cultural significance attached to these magnificent big cats. Journey through the conservation efforts aimed at safeguarding this rare and endangered species, ensuring their continued existence. Join us in celebrating the Asiatic Lion’s majestic presence in the wild and the collective efforts to preserve their legacy for generations to come.”
1. Historical Significance: Asiatic Lion
The Asiatic lion holds a special place in Indian history and culture. Depictions of lions can be found in ancient Indian art, symbolizing power and royalty. Over the centuries, however, the population of Asiatic lions declined, and by the early 20th century, they were on the brink of extinction, surviving only in the Gir Forest of Gujarat.
2. Unique Characteristics: Asiatic Lion
Asiatic lions, distinct from their African counterparts, exhibit unique characteristics. They often have a distinct fold of skin along their bellies and a less developed mane in males. Living in a habitat that includes dry deciduous forests, scrublands, and grassy plains, these lions have adapted to the challenging conditions of the Gir ecosystem.
3. Conservation Triumphs: Asiatic Lion
The Gir Forest has been the focal point of successful conservation efforts for the Asiatic lion. Strict protection measures, habitat management, and community involvement have led to a gradual increase in the lion population. The resilience of these big cats in the face of adversity stands as a testament to the effectiveness of dedicated conservation initiatives.
4. Conservation Challenges:
While the population of Asiatic lions has shown improvement, they still face challenges such as habitat fragmentation, disease outbreaks, and the potential for human-wildlife conflict. Expanding the conservation efforts beyond Gir and creating additional habitats are crucial steps in ensuring the long-term survival of this endangered species.
5. Coexistence and Community Involvement:
The success of Asiatic lion conservation is intricately linked to the involvement of local communities. Initiatives that promote coexistence, such as responsible tourism and sustainable development, not only benefit the lions but also contribute to the well-being of the communities living in proximity to their habitats.

Conclusion:
The Asiatic lion, with its regal presence and remarkable journey from the brink of extinction, symbolizes the triumph of conservation efforts in India. As custodians of this unique heritage, it is our responsibility to continue the work of preserving the Gir Forest and expanding the habitats for these majestic creatures. Through collective dedication and a shared commitment to coexistence, we can ensure that the roar of the Asiatic lion echoes through the arid landscapes of western India, inspiring awe and admiration for generations to come.